NMM/OMT
BRIEF REPORT
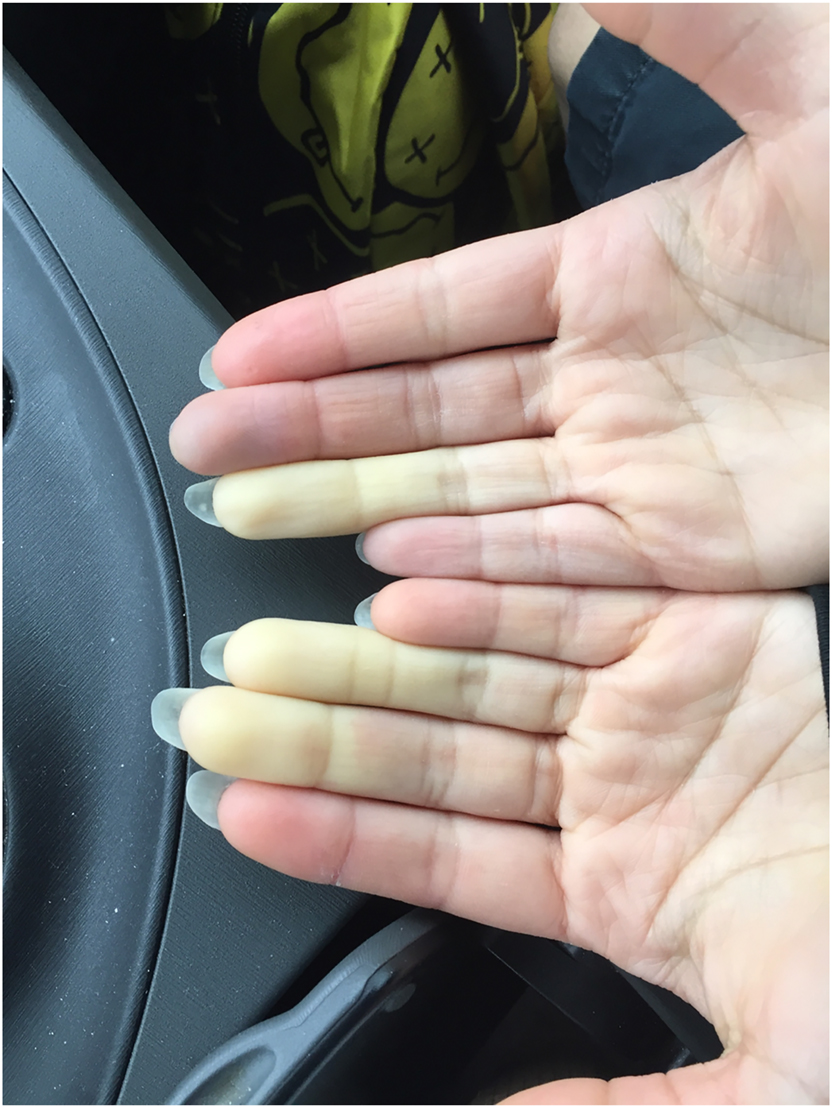
Augmentation of immune response to vaccinations through osteopathic manipulative treatment: a study of procedure
This article describes a proposed protocol to evaluate the effects of osteopathic manipulative treatment on antibody generation in the peripheral circulation in response to a vaccine and its possible …